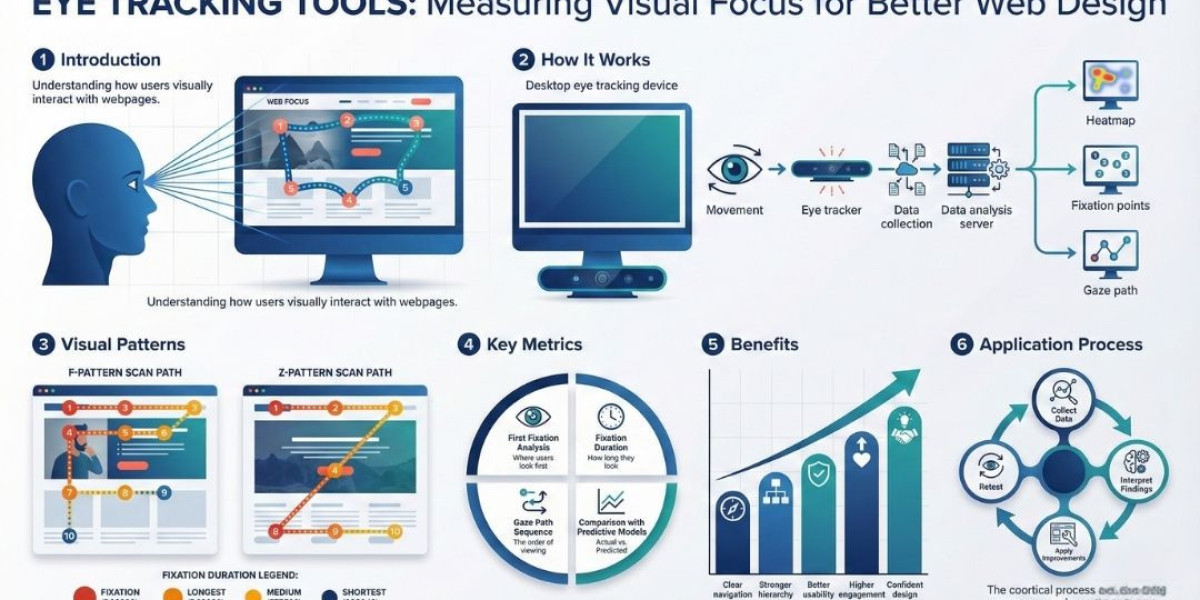
Understanding how users visually interact with a webpage is essential for improving clarity, usability, and overall structure. Visual focus analysis provides insights into where attention goes first, how users navigate content, and which elements may distract or confuse visitors. Rather than relying on assumptions or design intuition, measuring visual focus allows teams to make informed decisions backed by observable behavior.
Accurate visual focus assessment requires a structured approach that includes research tools, testing methods, interpretation techniques, and iterative refinement. By studying how the human eye responds to layout, typography, spacing, and hierarchy, designers and researchers can improve digital experiences and help visitors find what they need with less effort.
Why Measuring Visual Focus Matters
A webpage has only a few seconds to communicate value and direction. If the user cannot immediately identify what the page offers or how to move forward, confusion or disinterest may occur.
Measuring visual attention supports
Clear navigation
Stronger understanding of hierarchy
Better usability and readability
Higher engagement and progression
More confident design decisions
When a page aligns with natural visual behavior, users tend to explore more smoothly and stay longer.
How the Human Eye Responds to Digital Layouts
Visual movement across a screen is rarely random. Instead, it is influenced by cognitive processing, past experience, and design elements. In many cultures that read left to right, scanning patterns often follow structures such as the F or Z pattern. These patterns influence how headers, images, spacing, and calls to action should be placed.
Attention is strongly influenced by elements such as
Contrast and color balance
Typographic hierarchy
Whitespace distribution
Motion or animation
Image placement
Alignment and grouping
Recognizing these factors is essential before testing begins because they shape how users perceive structure.
Methods Used to Measure Visual Focus
Several approaches can reveal how users interact visually with a webpage. Each method offers different types of insight and may be used together for the most accurate results.
Observation and Task Based Testing
This approach involves watching how users interact with a design while completing specific tasks. Researchers take notes on hesitation, confusion, and eye movement patterns. Although useful, this method is not as precise as advanced tracking because subtle visual focus cannot always be observed manually.
Predictive Heatmap Models
Predictive heatmaps use algorithms to estimate where attention is most likely to go based on design structure. They are useful during early stages when prototypes are being shaped. These predictions guide layout refinement before live user testing.
Interaction Based Metrics
Click paths, scroll depth, and movement patterns can reveal where users attempt interaction and where they lose interest. While these metrics do not directly measure visual focus, they help confirm navigation clarity and content relevance.
Advanced Visual Tracking Research
This method provides the most accurate understanding of visual behavior. It records where users look, how long they focus, and the sequence of their gaze. An eye tracking tool can reveal subconscious patterns and highlight which elements capture or fail to capture attention.
Interpreting Visual Attention Findings
Collecting data is only the beginning. To make improvements, the findings must be interpreted correctly and linked to design objectives.
Key interpretation principles include
First Fixation Analysis
The point where the eye first lands shows the strongest natural draw. Ideally, this should align with the most important message or primary navigation element.
Fixation Duration
Long fixations may indicate complex content or confusion. Shorter grouped fixations may indicate scanning behavior. Evaluating duration patterns helps determine whether messaging is clear or overwhelming.
Gaze Path and Sequence
Understanding the order of attention helps verify whether the intended flow aligns with user behavior. If users jump around unpredictably or skip key content, layout adjustments may be needed.
Comparison With Predictive Models
Matching predictive analysis with real user data can reveal whether early assumptions were accurate or require refinement.
Applying Results to Improve Web Design
Once patterns are identified, adjustments can be made to improve structure, clarity, and flow. These improvements may include
Adjusting hierarchy to highlight key messages
Increasing whitespace to avoid crowding
Relocating important interactive elements
Reducing unnecessary decorative content
Improving contrast for readability
After refinement, retesting ensures the adjustments meet the intended objectives.
Balancing User Data With Creative Design
While data provides valuable insight, design should remain aligned with brand tone, message, and purpose. Not every adjustment must follow testing results exactly. Instead, research should serve as guidance that informs decision making without removing creativity.
A long term approach that includes continuous testing, refinement, and validation creates a more consistent and user friendly experience over time.
Final Thoughts
Measuring visual focus plays a meaningful role in building websites that feel intuitive and comfortable to explore. It helps identify which elements attract attention, where confusion appears, and whether the structure supports the intended user journey. Using an eye tracking tool not only captures attention patterns but also supports testing that aligns design decisions with observed behavior. When combined with thoughtful analysis and iterative refinement, visual focus research creates stronger digital experiences where clarity meets purpose and every element supports usability.
FAQs
1. What is visual focus analysis
It is the study of how users visually interact with a webpage to understand attention patterns.
2. Can visual focus be tested during early design stages
Yes, predictive tools and prototype testing can be used before final development.
3. How many participants are needed for effective testing
A small group can reveal patterns, while larger groups offer broader validation.
4. Does scrolling behavior show visual attention
It indicates engagement but does not reflect exact focus without additional tracking.
5. Should testing be repeated after design updates
Yes, repeating tests ensures that new layouts still support clear user flow.